Ansible vs Jenkins: Choosing the Right Tool for Your Automation Needs
Ansible and Jenkins stand out as two titans, each with its own unique strengths. Ansible excels in configuration management and automating IT tasks, while Jenkins shines in continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
In the realm of automation tools, Ansible and Jenkins stand out as two titans, each with its own unique strengths. Ansible excels in configuration management and automating IT tasks, while Jenkins shines in continuous integration and continuous delivery (CI/CD) pipelines. The right choice largely depends on the specific needs of your projects.

Understanding Ansible and Its Features
Ansible is an open-source automation tool primarily used for configuration management, application deployment, and task automation. Written in Python, it uses a declarative language to describe the desired state of the system.
Key Features of Ansible:
- Agentless Architecture: No need for agent installation on managed nodes; it operates over SSH or WinRM.
- Playbooks: Configurations are defined in simple YAML files that detail the desired state.
- Idempotency: Ensures tasks can be run multiple times without altering the outcome beyond the initial application.
- Extensibility: Easily extendable with custom modules, adaptable to various environments.
- Integration: Seamlessly integrates with various cloud providers, monitoring tools, and DevOps tools.
When to Use Ansible:
Choose Ansible when you need to manage configurations across many servers, deploy applications consistently, automate repetitive tasks, or prefer a declarative syntax with YAML. Leveraging Ansible can significantly enhance operational efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
Diving into Jenkins and Its Offerings
Jenkins is a widely-used open-source automation server that automates parts of software development related to building, testing, and deploying applications. Built in Java, it runs on various environments.
Key Features of Jenkins:
- Plugins: Boasts a rich ecosystem of plugins, allowing integration with virtually any tool in the software delivery ecosystem.
- Declarative and Scripted Pipelines: Supports two types of pipeline definitions, offering flexibility in defining CI/CD processes.
- Distributed Builds: Can distribute workloads across multiple machines, improving build performance.
- Easy Configuration: User-friendly UI for easy setup and configuration of pipelines.
- Extensive Community Support: Large user base ensures finding help or documentation is often straightforward.
When to Use Jenkins:
Opt for Jenkins if you need robust CI/CD capabilities, run frequent automated tests, benefit from a strong community, or require integration with numerous third-party services. Jenkins can enhance the development lifecycle, leading to faster releases and high-quality software.
Comparing Ansible and Jenkins: Key Differences

Here’s a comparative overview to help you make an informed decision:
| Feature | Ansible | Jenkins |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Focus | Configuration management and task automation | Continuous integration and delivery |
| Architecture | Agentless, uses SSH/WinRM | Uses agents, requires more setup |
| Usability | Easier due to YAML and declarative approach | Steeper learning curve with complex plugins |
| Integrated Workflows | Easily integrates with CI/CD tools | Manages CI/CD processes and execution flow |
| Automation Efficiency | Ideal for repetitive configuration tasks | Powerful in automating build, test, deploy workflows |
Leveraging Both Ansible and Jenkins
In many cases, using both tools together can create a powerful automation setup. Here’s how they can complement each other:
Integrated Workflows:
- Jenkins for CI/CD: Manage build processes, orchestrate tests, and deploy applications.
- Ansible for Deployment: Configure and manage the production environment post-deployment.
Enhanced Automation:
Using Jenkins with Ansible allows teams to:
- Create a holistic automation process
- Eliminate repetitive tasks
- Ensure consistent environments with Ansible’s configuration management capabilities
Why Integrate?
- Streamlined Automation: Simplifies management of complex workflows.
- Flexibility and Control: Optimal tool for each task.
- Resource Efficiency: Reduces deployment and update time.
Real-World Applications of Ansible and Jenkins
Success Stories
Tech giants leverage Ansible and Jenkins to streamline DevOps practices, improving deployment times and system reliability. Using both has helped businesses implement robust continuous deployment strategies, reducing the time to market.
Case Example: EchoAPI
Imagine a fictional company, EchoAPI, using both tools strategically. The development team relies on Jenkins for CI processes, automating builds and tests. For deployments, they switch to Ansible, leveraging its capabilities to consistently configure servers across environments.
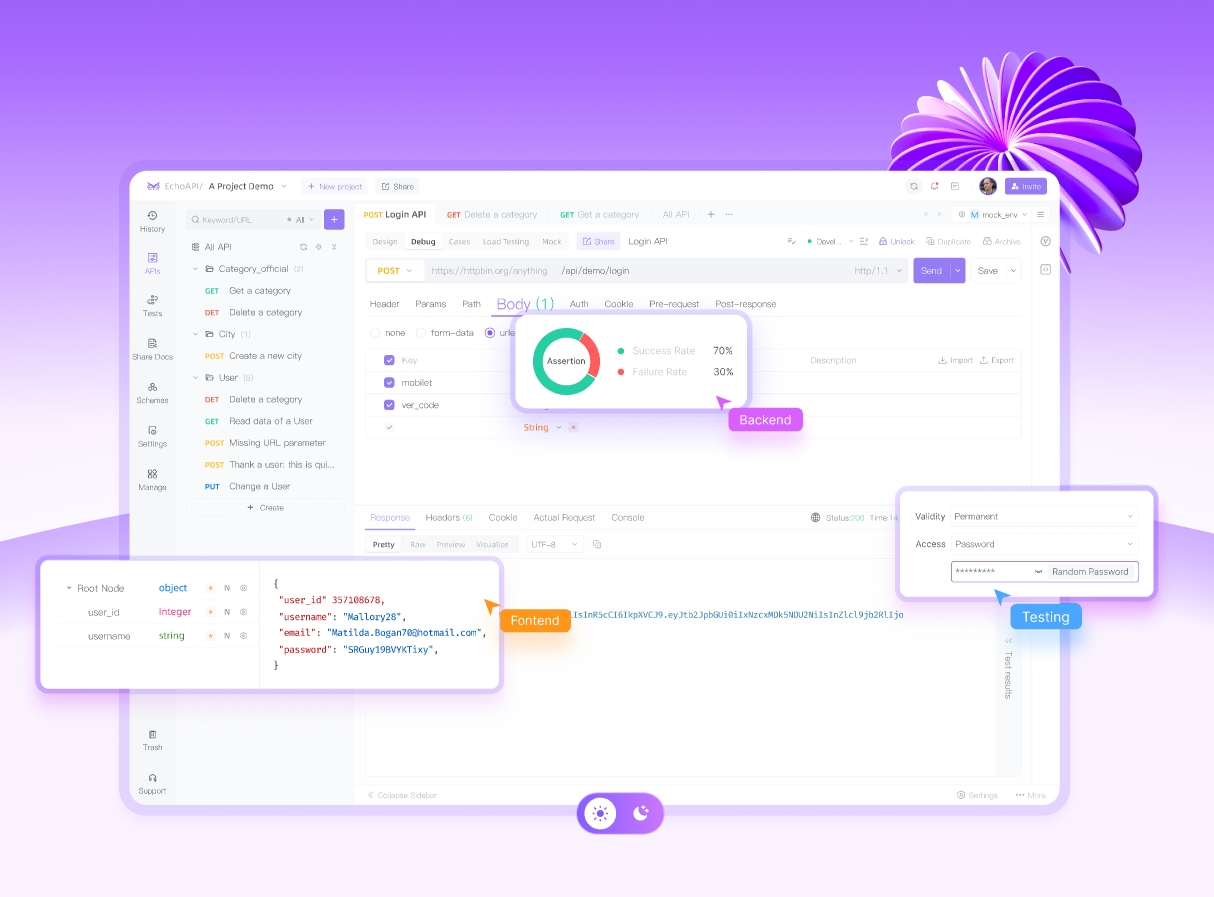
Outcome: By integrating both tools, EchoAPI reduced downtime during deployments, improved developer productivity, and ensured high-quality software releases.
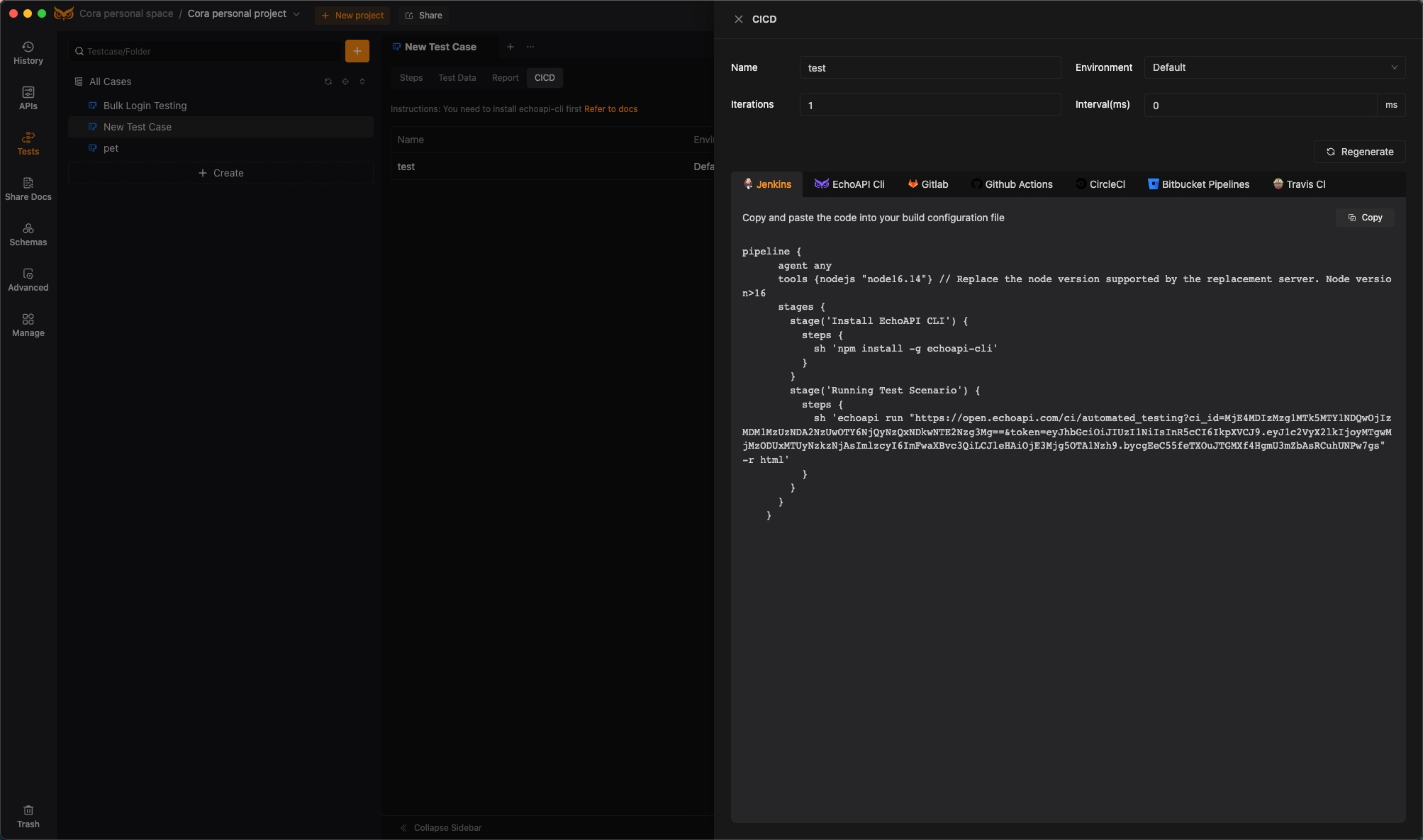
Making the Right Choice for Your Team
The decision between Ansible and Jenkins depends on your project needs:
- Choose Ansible for configuration management, deployment automation, and managing large-scale infrastructure.
- Opt for Jenkins for implementing CI/CD practices, running automated tests, and integrating with various services.
Conclusion
Both Ansible and Jenkins are robust tools that can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your software development lifecycle. Understanding their distinct features and use cases enables you to make informed decisions on incorporating them into your workflows. Whether employing one or both, embracing automation will streamline development processes, enhance team productivity, and lead to better software outcomes.




 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server








