Python Requests: How to POST JSON Data with Ease in 2024
In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn how to use the Python Requests library to send JSON data as a POST request.
In this comprehensive guide, you'll learn how to use the Python Requests library to send JSON data as a POST request. With step-by-step instructions and practical examples, you'll be able to perform efficient and effective API calls. Let's dive in and enhance your Python skill set!
Introduction to Python Requests
Python Requests is a user-friendly library for sending HTTP requests in Python. It supports all HTTP methods, including GET, POST, PUT, DELETE, and more. For Python 3.7 and above, it simplifies the process of interacting with web services.

Making a POST Request
Here's a simple example of making a POST request using Python Requests:
import requests
url = 'https://www.example.com/api'
data = {'username': 'my_username', 'password': 'my_password'}
response = requests.post(url, data=data)
print(response.status_code)
print(response.text)
In this example, an HTTP POST request is sent to https://www.example.com/api with a payload containing a username and password. The response's status code and content are then printed to the console.
Installing the Requests Library
To install Python Requests, use the following command:
pip install requests
Understanding JSON 📊
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) is a lightweight data-interchange format that's easy for humans to read and write, and easy for machines to parse and generate. JSON is language-independent and widely used for data exchange in web applications.

Example JSON Object
{
"id": 1001,
"title": "What is JSON?",
"author": {
"id": 1,
"name": "John Doe"
},
"tags": ["api", "json", "programming"],
"published": false,
"publishedTimestamp": null
}
This JSON object represents a simple blog post, showcasing various data types such as strings, numbers, booleans, null, arrays, and nested objects.
Sending JSON Data in a POST Request
Now, let's see how to send JSON data in a POST request:
import requests
import json
url = 'https://www.example.com/api'
data = {'username': 'my_username', 'password': 'my_password'}
headers = {'Content-type': 'application/json'}
response = requests.post(url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers)
print(response.status_code)
print(response.text)
In this example, we convert the data dictionary to a JSON string using json.dumps() and include Content-type: application/json in the request headers.
Simplified JSON POST
Python Requests also allows you to send JSON data directly using the json parameter:
import requests
url = 'https://www.example.com/api'
data = {'username': 'my_username', 'password': 'my_password'}
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
print(response.status_code)
print(response.text)
This method eliminates the need for json.dumps() and simplifies the code.
Handling Responses
After sending a POST request, handle the response as follows:
import requests
url = 'https://www.example.com/api'
data = {'username': 'my_username', 'password': 'my_password'}
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
if response.status_code == 200:
print('Success!')
print(response.json()) # If the response contains JSON data
else:
print('An error occurred:', response.status_code)
Check the response status code to determine if the request was successful (usually indicated by a status code of 200).
Handling Errors Gracefully
To handle errors during the HTTP request, use a try-except block:
import requests
url = 'https://www.example.com/api'
data = {'username': 'my_username', 'password': 'my_password'}
try:
response = requests.post(url, json=data)
response.raise_for_status()
except requests.exceptions.HTTPError as err:
print('HTTP error occurred:', err)
except Exception as err:
print('An error occurred:', err)
This approach ensures that your program can handle unexpected issues gracefully.
How to Send Python POST Requests with JSON Data in EchoAPI
EchoAPI is an advanced API debugging tool designed for efficient API testing and continuous monitoring. By integrating EchoAPI into your workflow, you can automate performance tests and catch potential issues early in your development process. Here’s how to seamlessly send a Python POST request with JSON data using EchoAPI.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using EchoAPI for POST Requests
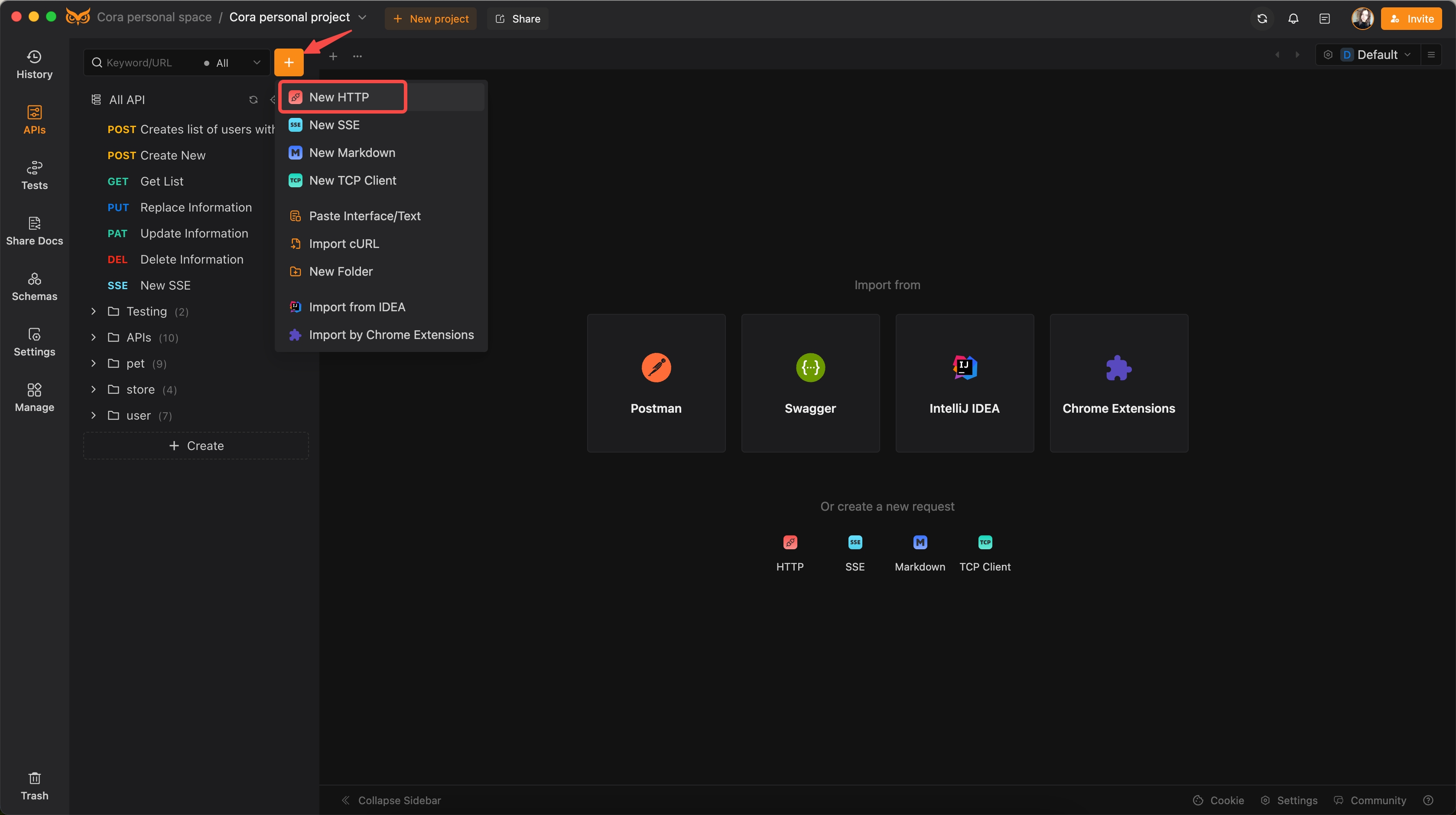
Step 1: Create a New HTTP Request
- Open EchoAPI.
- Click on the "New HTTP" button to create a new request.
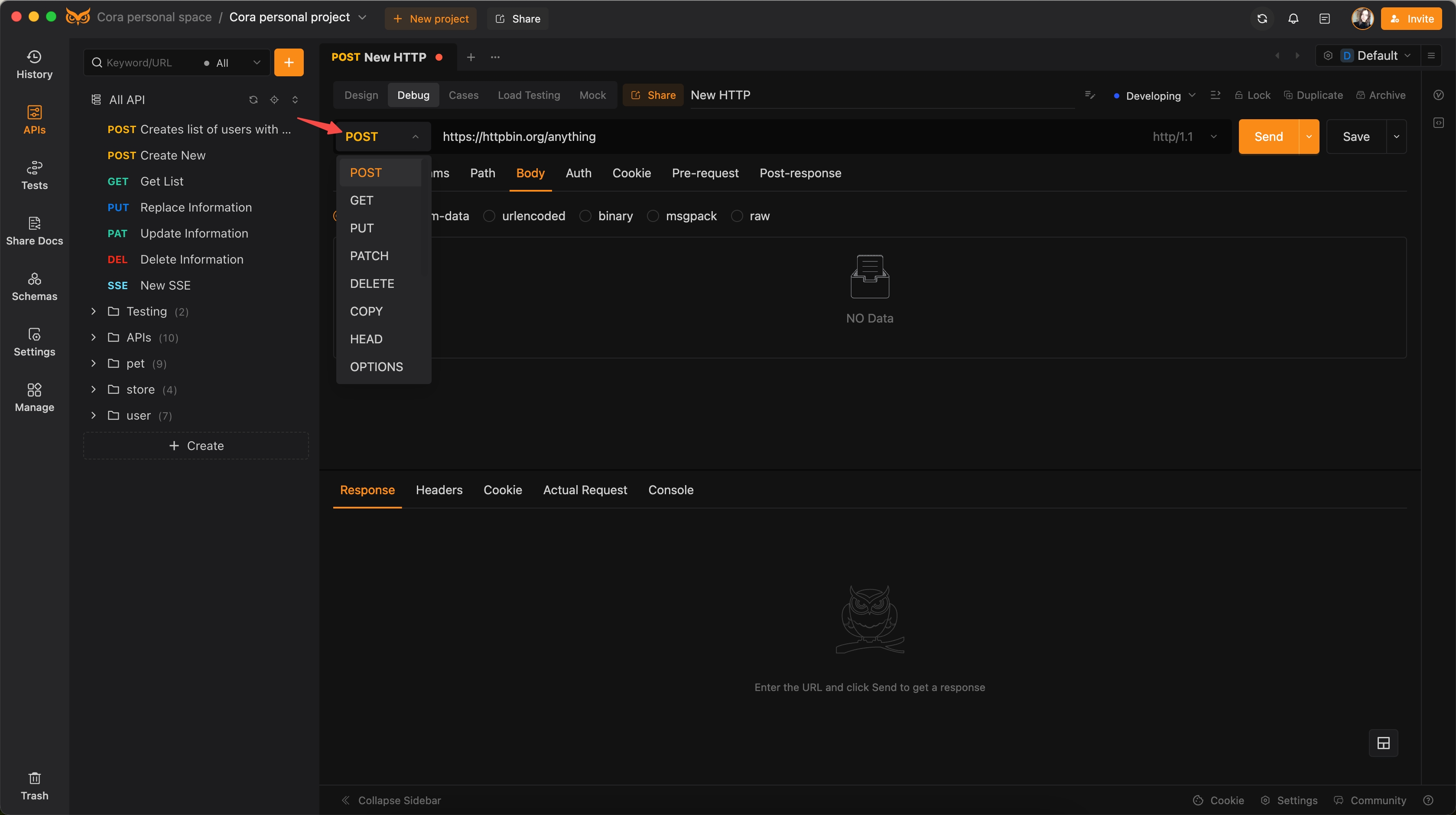
Step 2: Select the HTTP Method
- Choose the appropriate request method. For this tutorial, select
POST.
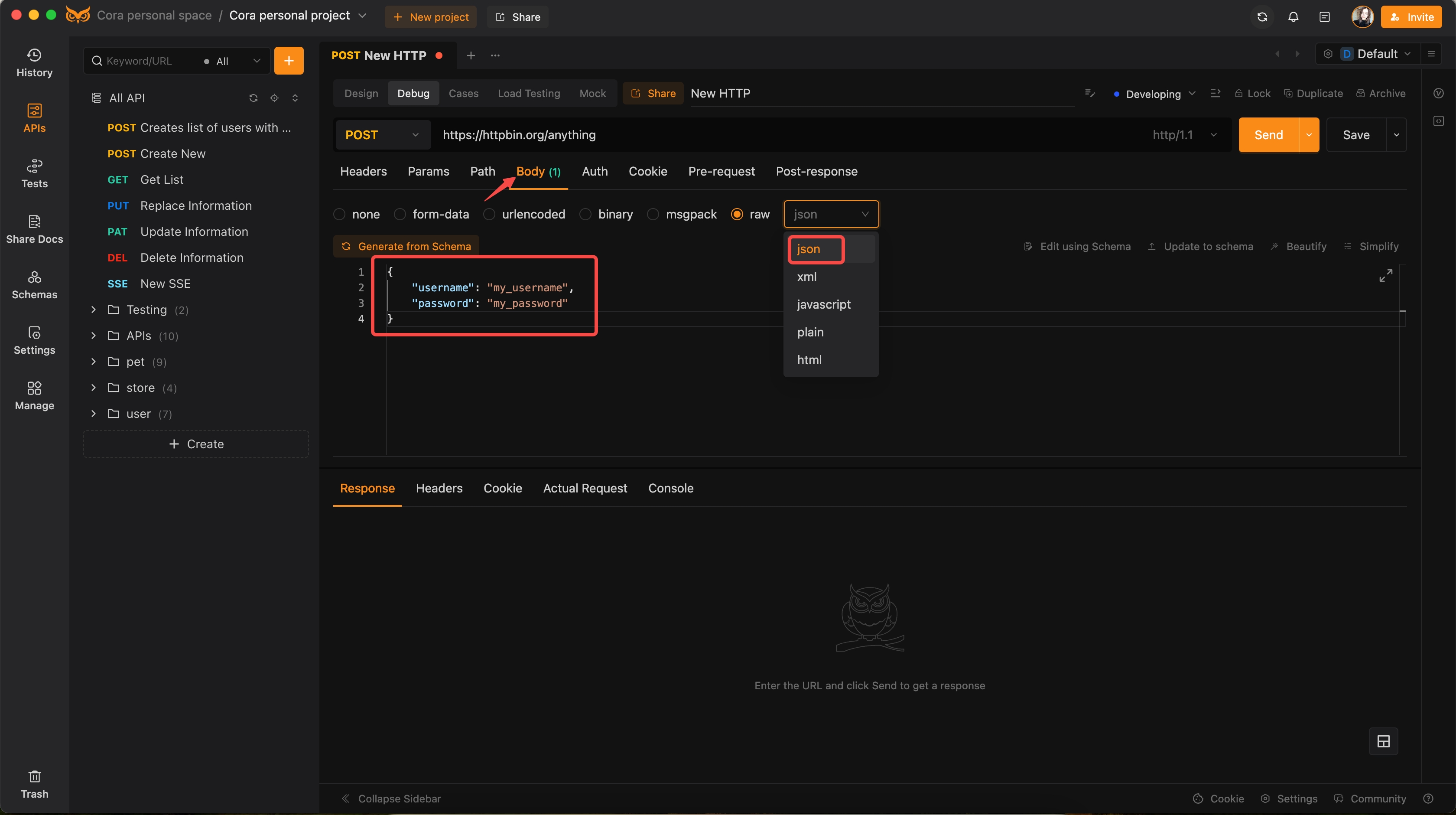
Step 3: Set Up the Request Body
- Navigate to the
Bodysection of the request. - Select
rawfrom the available formats. - Choose
jsonfrom the dropdown menu.
Enter your JSON data in the provided text area. Here’s an example:
{
"username": "my_username",
"password": "my_password"
}
Step 4: Send the Request and View Results
- Click the
sendbutton to dispatch your request. - Review the response to check the status code and data returned by the server.
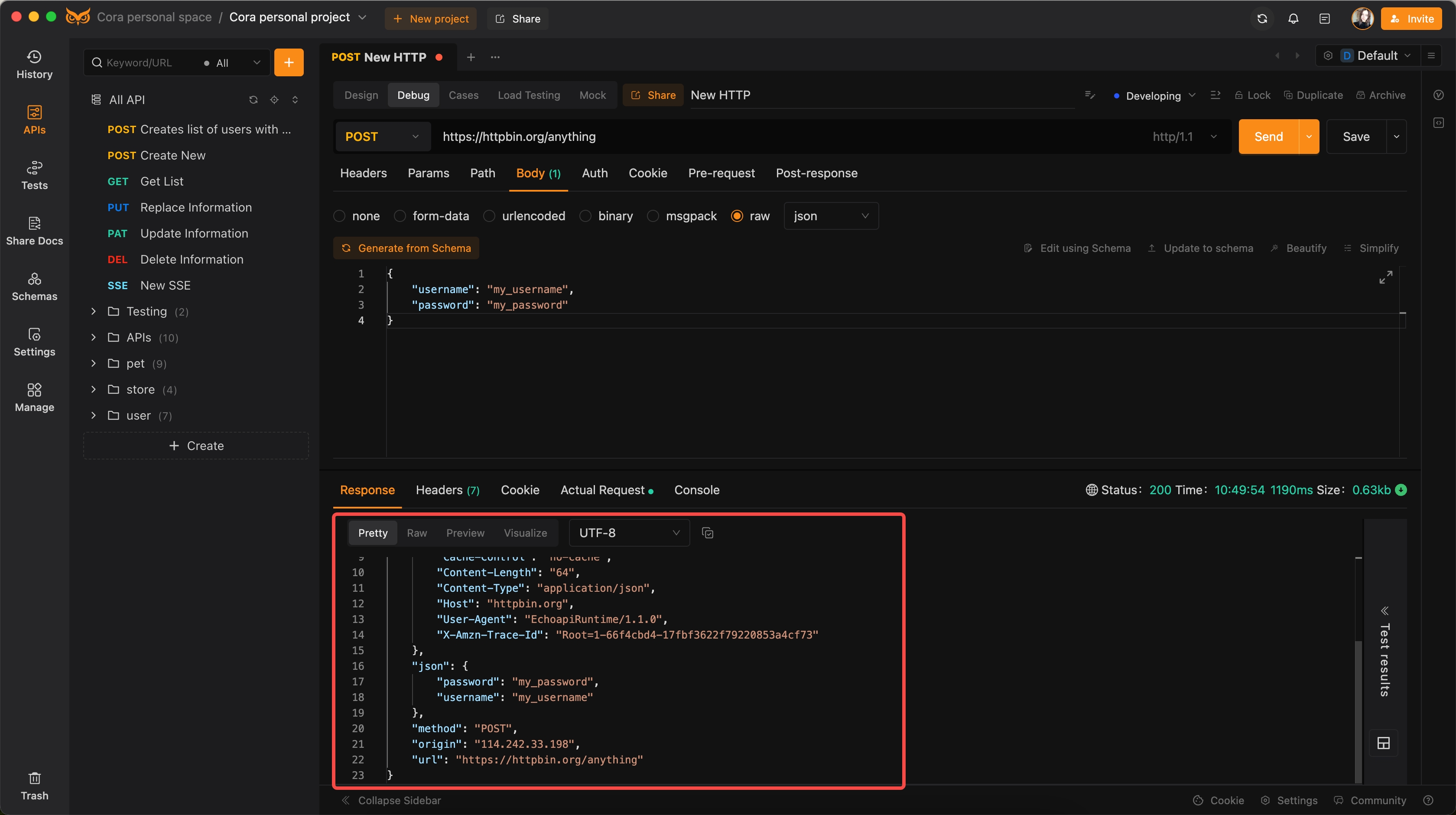
That's it! You have successfully sent a Python POST request with JSON data using EchoAPI.
Conclusion 🏁
In this post, we've covered how to use Python Requests to send JSON data via POST requests. We explored the basics of JSON, making POST requests, handling responses, and managing errors. Additionally, we introduced EchoAPI as a powerful tool for automating and optimizing your API testing workflow.
By mastering these techniques, you'll be well-equipped to handle HTTP requests in Python efficiently and effectively. Happy coding! 🎉









 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server




