The Difference Between Basic Auth and Bearer Token: Which API Tool Should You Choose?
This article explores the significance of authentication, introduces Basic Auth and Bearer Token, compares the two methods, provides use cases for each, and demonstrates how to implement them.
In the evolving landscape of web development, secure API authentication is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring that only authorized users can access specific endpoints. This article explores the significance of authentication, introduces Basic Auth and Bearer Token, compares the two methods, provides use cases for each, and demonstrates how to implement them using EchoAPI.
The Significance of Authentication
Authentication is a fundamental aspect of API security. It ensures that the clients accessing the API are who they claim to be, thereby preventing unauthorized access and protecting sensitive information. Authentication mechanisms also contribute to accountability and auditability by tracking who accessed what data and when.
Introduction to Basic Auth and Bearer Token
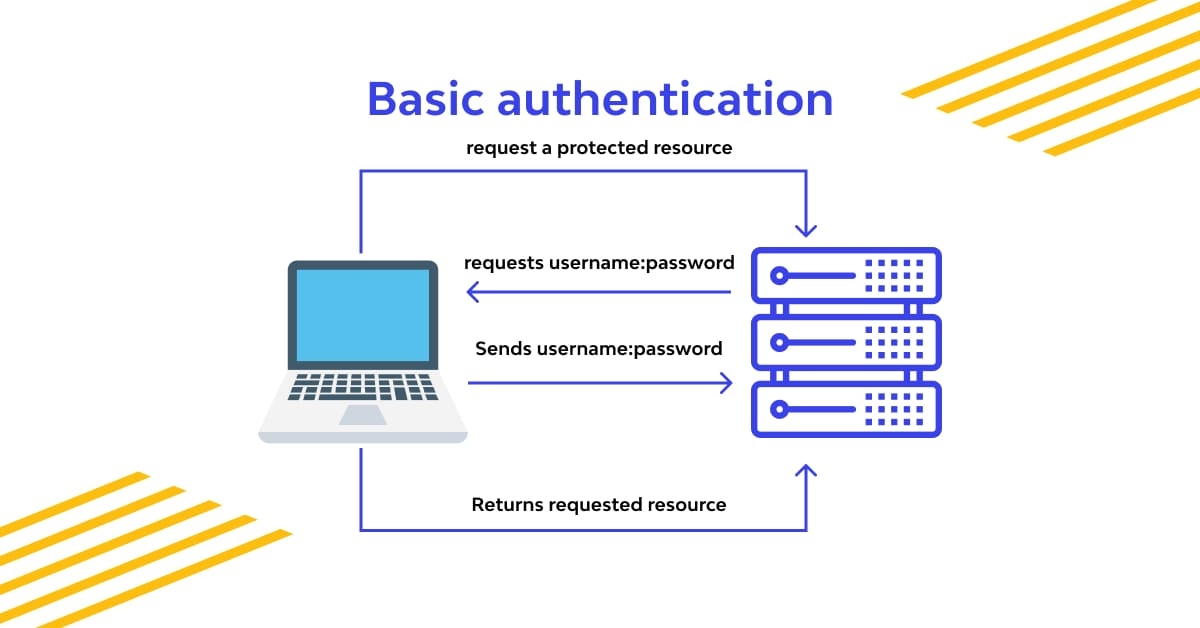
Basic Auth
This method involves sending a base64-encoded string containing the username and password with each request. Despite its simplicity and ease of use, Basic Auth is less secure because the credentials are sent with every request and can be easily intercepted if not encrypted using HTTPS.
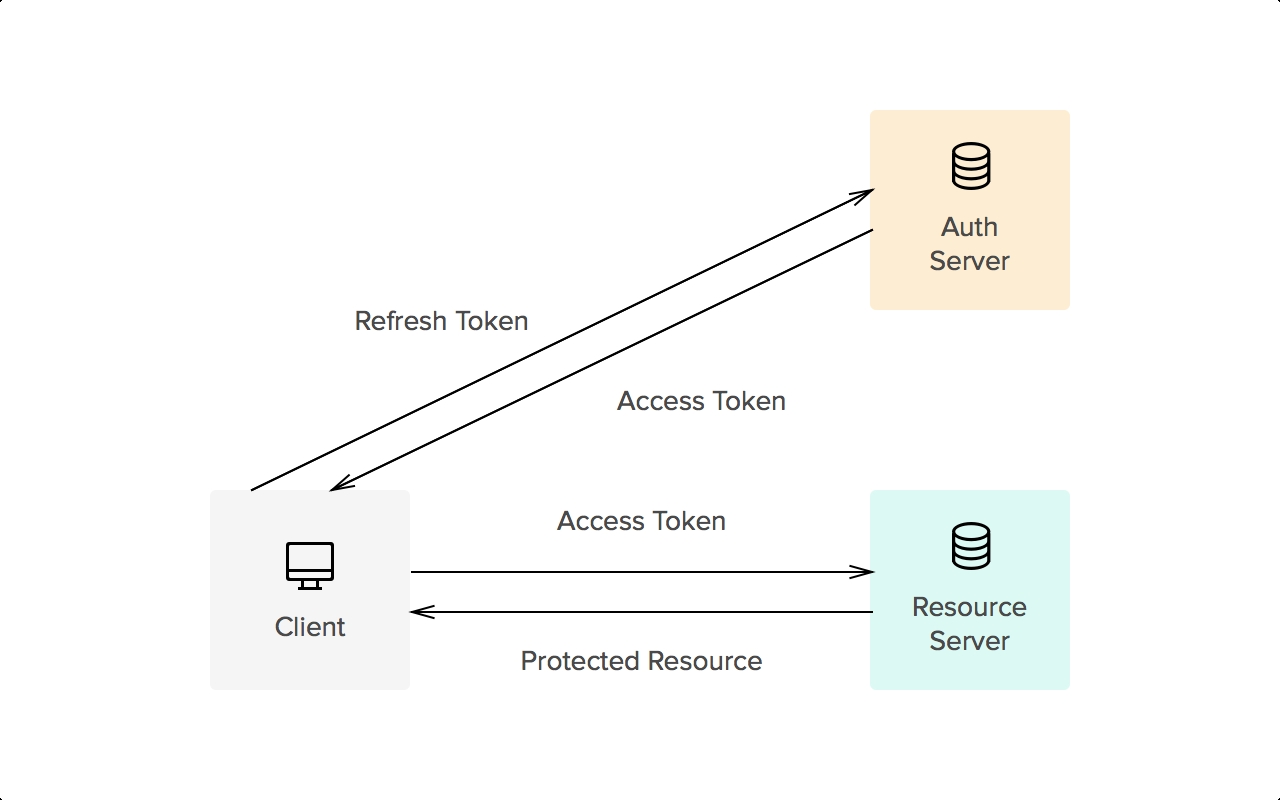
Bearer Token
Commonly used in OAuth 2.0, this method involves sending a token with each request. The token represents a user's authenticated session and provides more security since it can be set to expire and is not tied directly to the user's credentials.
Comparing Basic Auth and Bearer Token
Security
- Basic Auth: Sends username and password with every request, which can be risky if intercepted.
- Bearer Token: Uses a token that can be more securely and temporarily managed.
Ease of Use
- Basic Auth: Simple to implement but requires managing user credentials.
- Bearer Token: Slightly more complex but provides better security and flexibility.
Session Management
- Basic Auth: No session management; credentials are validated with every request.
- Bearer Token: Supports session expiration and renewal, offering better control over user sessions.
Implementation
- Basic Auth: Requires only base64 encoding of credentials and adding to the request header.
- Bearer Token: Involves generating and managing tokens, typically requiring additional backend support.
Which to Use: Practical Examples
When to Use Basic Auth
- Example: A small internal tool where simplicity is more critical than high security.
GET /protected/resource HTTP/1.1
Host: example.com
Authorization: Basic YWxhZGRpbjpvcGVuc2VzYW1l
When to Use Bearer Token
- Example: A public API that requires robust security measures.
GET /user/profile HTTP/1.1
Host: api.example.com
Authorization: Bearer your_token
Setting Up Auth with EchoAPI
EchoAPI makes it effortless to manage and test various API authentication methods. Follow these steps for efficient setup:
1. Create or Import a Request
- Begin by creating a new request or importing an existing one into EchoAPI.

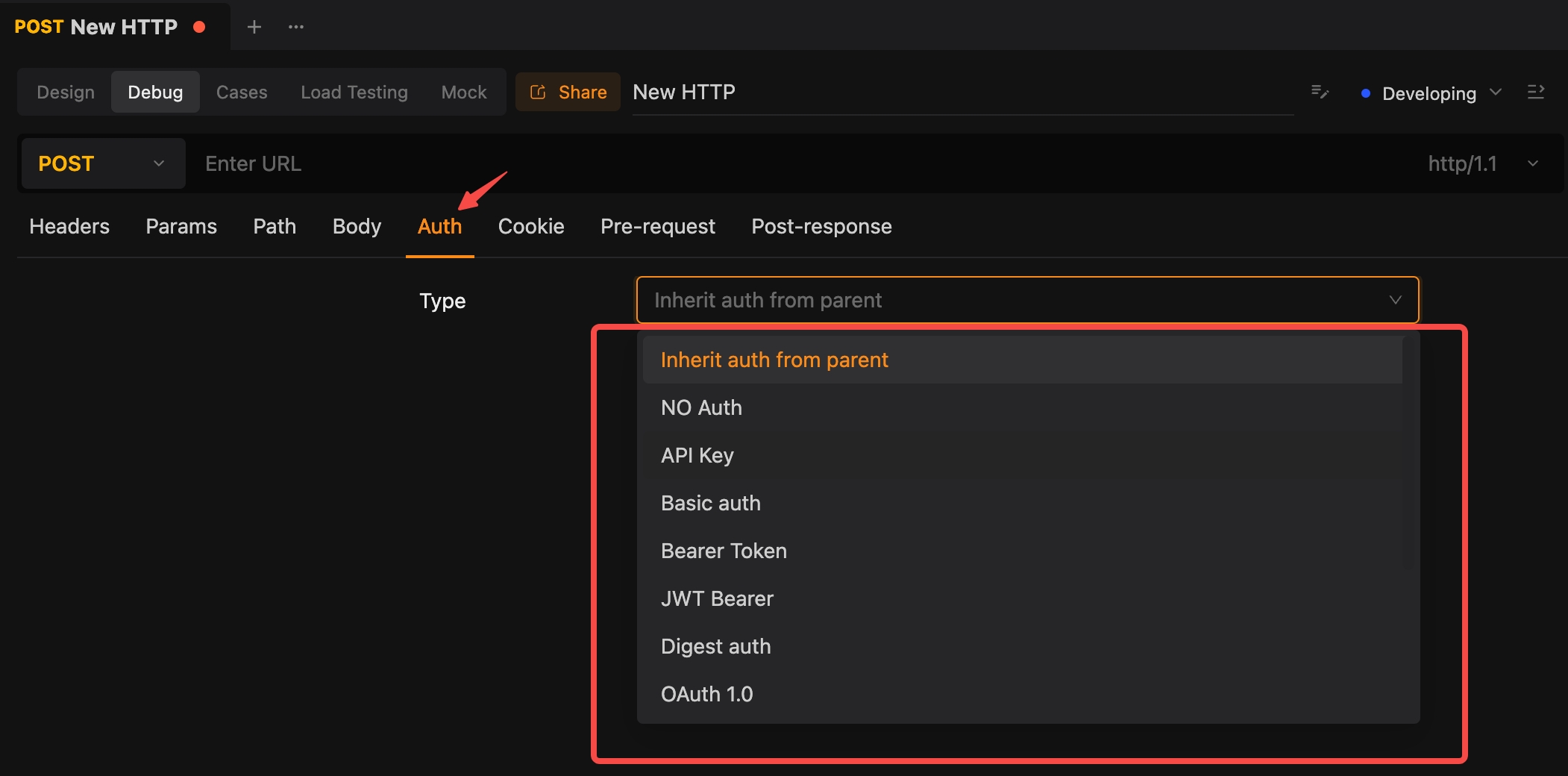
2. Set Up Authentication
- Navigate to the authentication section within the request setup.
- Select the appropriate authentication type (e.g., Basic, Bearer).
- Enter the necessary credentials or tokens.
3. Execute Requests
- Send the request and carefully inspect the response to verify that the authentication was successful.
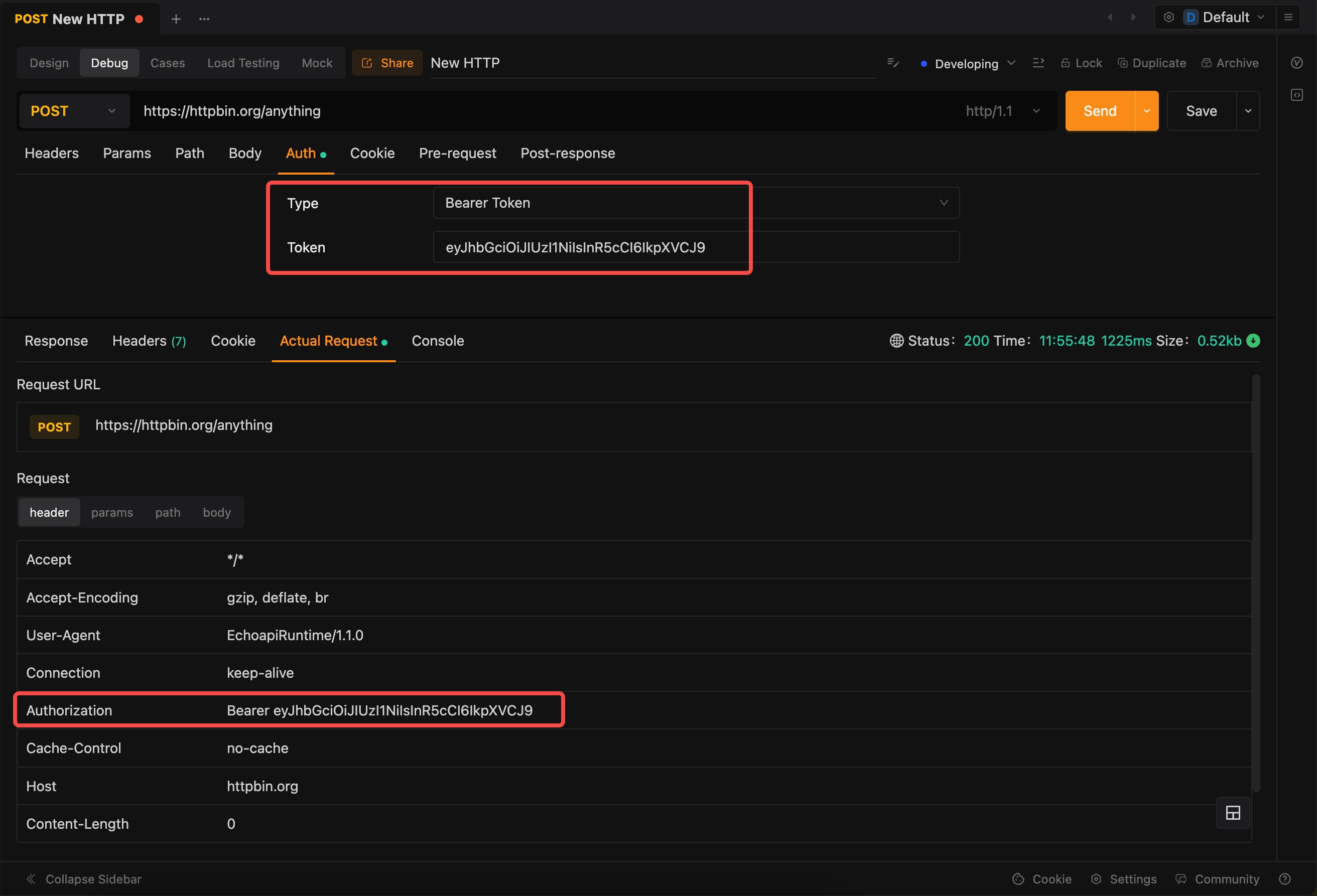
By following these steps, EchoAPI ensures a streamlined process for setting up, managing, and testing your API authentication methods.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Basic Auth | Bearer Token |
|---|---|---|
| Security | Low (credentials sent on every request) | High (tokens can expire, no user details) |
| Ease of Use | Easy | Moderate |
| Session Mgmt | None | Supports sessions |
| Implementation | Simple (base64 encode credentials) | Requires backend support for token management |
| Use Cases | Internal, simple tools | Public APIs needing more security |
Conclusion
Choosing between Basic Auth and Bearer Token depends on your API's specific requirements. Basic Auth is suitable for simple, low-security scenarios, while Bearer Token provides higher security and better session management for more complex and public APIs. Tools like EchoAPI facilitate the implementation and testing of these authentication methods, ensuring your API remains secure and performant. By understanding and applying the right authentication strategy, you can enhance the security and user experience of your APIs.




 EchoAPI for VS Code
EchoAPI for VS Code

 EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA
EchoAPI for IntelliJ IDEA

 EchoAPl-Interceptor
EchoAPl-Interceptor

 EchoAPl CLI
EchoAPl CLI
 EchoAPI Client
EchoAPI Client API Design
API Design
 API Debug
API Debug
 API Documentation
API Documentation
 Mock Server
Mock Server








